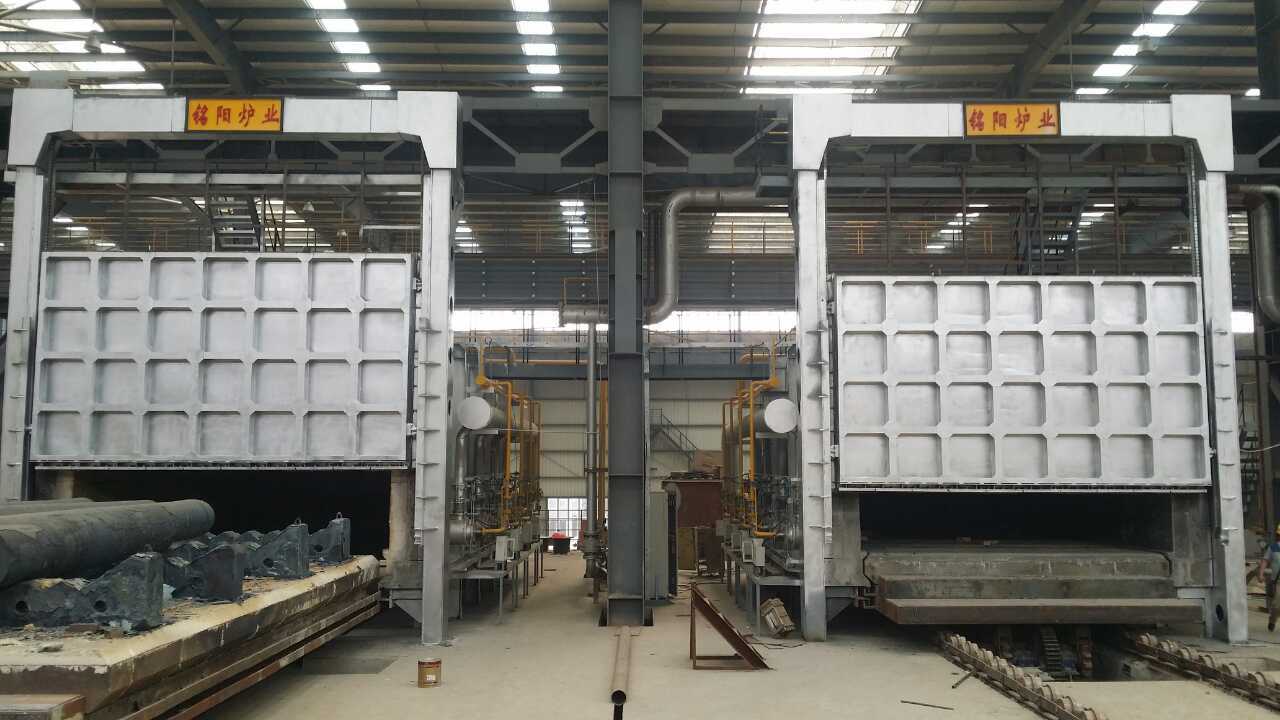
Durable Quenching Furnaces: An Essential Component of Metal Production
Understanding Durable Quenching Furnaces in Metal Production
Quenching furnaces play a pivotal role in the metal production industry, particularly in the field of heat treatment. These specialized furnaces are designed to rapidly cool hot metal components after they have been heated to specific temperatures during various processes, such as forging, casting, or machining. The durability and operat
Understanding Durable Quenching Furnaces in Metal Production
Quenching furnaces play a pivotal role in the metal production industry, particularly in the field of heat treatment. These specialized furnaces are designed to rapidly cool hot metal components after they have been heated to specific temperatures during various processes, such as forging, casting, or machining. The durability and operational efficiency of quenching furnaces directly influence the quality of the final metal products, making them essential in any manufacturing environment.
In this comprehensive article, we delve into the intricacies of durable quenching furnaces, exploring their types, benefits, and best practices in operation.
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Quenching Furnaces
- 2. Types of Quenching Furnaces
- 3. Benefits of Using Durable Quenching Furnaces
- 4. How Quenching Furnaces Operate
- 5. Key Factors That Affect Performance
- 6. Maintenance Tips for Longevity
- 7. Safety Considerations in Quenching
- 8. Conclusion
- 9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Introduction to Quenching Furnaces
The process of quenching involves cooling hot metals at controlled rates to achieve desired mechanical properties, such as strength and hardness. Quenching furnaces facilitate this process by providing a controlled environment through which metal components can be cooled efficiently.
These furnaces can vary significantly in design and functionality, tailored to meet the specific needs of different industries, from automotive to aerospace manufacturing. Understanding their role is crucial for any business that relies on high-quality metal parts.
2. Types of Quenching Furnaces
There are several types of quenching furnaces, each designed for specific applications. Knowing the differences can help manufacturers choose the right furnace for their operations.
2.1 Batch Quenching Furnaces
Batch quenching furnaces are designed to process metal parts in groups or batches. They are typically used for smaller production runs and allow for flexibility in the types of parts being treated. The main advantage of batch quenching is the ability to accommodate various sizes and shapes of components without significant alteration to the furnace setup.
2.2 Continuous Quenching Furnaces
Continuous quenching furnaces are designed for high-volume production where metal parts move through the furnace on a conveyor system. This type is ideal for large-scale manufacturing runs, providing consistent heating and cooling rates, which leads to uniformity in product quality. Manufacturers often employ continuous quenching furnaces for processes such as wire and bar production.
2.3 Modular Quenching Furnaces
Modular quenching furnaces offer a flexible design that can be expanded as production needs grow. They are particularly beneficial for facilities that anticipate changes in production volume or variety. The modular design allows for easy upgrades and modifications without extensive overhauls of the entire system.
3. Benefits of Using Durable Quenching Furnaces
Investing in durable quenching furnaces provides several advantages that can affect the overall efficiency and quality of metal production.
3.1 Enhanced Product Quality
Durable quenching furnaces ensure precise temperature control during the cooling process, which directly impacts the metallurgical properties of the finished product. This results in better tensile strength, toughness, and resistance to wear.
3.2 Increased Production Efficiency
By optimizing cooling times and processes, durable quenching furnaces help reduce cycle times, enabling manufacturers to produce more parts in less time. The efficiency of these furnaces contributes significantly to overall operational productivity.
3.3 Cost-Effective Operation
Durability translates to lower maintenance and repair costs. Investing in a high-quality quenching furnace can lead to significant savings over time, as less frequent breakdowns and repairs mean less downtime and operational disruptions.
3.4 Improved Safety Standards
Modern quenching furnaces are designed with safety features that protect operators and reduce the risk of accidents. Robust construction and automated controls contribute to a safer work environment, which is essential in any industrial setting.
4. How Quenching Furnaces Operate
Understanding the operational mechanics of quenching furnaces can help manufacturers appreciate their role in the metal production process.
4.1 Heating Phase
The process begins with heating metal parts to a predetermined temperature, usually above their critical temperature. This heating phase is crucial for achieving the desired metallurgical changes before quenching.
4.2 Quenching Phase
Once the metal reaches the appropriate temperature, it is introduced into the quenching medium—this can be water, oil, or specialized quenching fluids. The choice of medium significantly affects cooling rates and the resulting material properties.
4.3 Cooling Phase
The cooling phase is critical for determining the final mechanical properties of the metal. The rate of cooling must be carefully controlled to avoid thermal shock, which can result in cracking or warping.
4.4 Post-Quenching Treatment
After quenching, metal parts may undergo additional processes, such as tempering or aging, to further refine their mechanical properties. These steps ensure that the finished product meets the specific requirements of the intended application.
5. Key Factors That Affect Performance
Several factors influence the performance of quenching furnaces and the effectiveness of the quenching process.
5.1 Material Type
Different metals and alloys have unique properties and respond differently to heat treatment. Understanding the specific requirements for each material type is crucial for optimizing furnace performance.
5.2 Quenching Medium
The choice of quenching medium affects cooling rates and the properties of the final product. Manufacturers must select an appropriate medium based on the metal being treated and desired outcomes.
5.3 Temperature Control
Precise temperature control is vital for achieving consistent results. Any deviation from the required temperature can lead to undesirable changes in the metal's properties.
5.4 Furnace Design
The design of the quenching furnace, including insulation, airflow, and heating elements, plays a crucial role in its efficiency and effectiveness. A well-designed furnace can significantly improve operational performance.
6. Maintenance Tips for Longevity
To ensure the longevity and optimal performance of quenching furnaces, routine maintenance is essential. Here are some best practices:
6.1 Regular Inspections
Conduct regular inspections of the furnace components, including heating elements, insulation, and electrical systems. Address any wear or damage promptly to prevent costly repairs.
6.2 Clean the Quenching Medium
Contaminants in the quenching medium can affect cooling rates and product quality. Regularly check and replace the quenching fluid as needed to maintain its efficacy.
6.3 Monitor Temperature Controls
Routine calibration of temperature controls ensures that the furnace operates within the specified parameters. This helps maintain consistency in the heat treatment process.
6.4 Staff Training
Proper training for staff operating the quenching furnaces is essential. Ensure that employees understand the importance of following protocols and maintaining safety standards.
7. Safety Considerations in Quenching
Safety is paramount in any industrial environment, and quenching furnaces present unique challenges.
7.1 Protective Gear
Operators should always wear appropriate protective gear, including heat-resistant clothing, gloves, and eye protection, to minimize the risk of burns and other injuries.
7.2 Emergency Protocols
Establish clear emergency protocols to address potential hazards associated with the quenching process. Regular drills can help ensure that staff are prepared for emergencies.
7.3 Ventilation Systems
Adequate ventilation is crucial to prevent the buildup of fumes and vapors that may be released during the quenching process. Ensure that proper exhaust systems are in place and functioning effectively.
8. Conclusion
Durable quenching furnaces are essential components of metal production, playing a critical role in enhancing the quality, efficiency, and safety of metalworking processes. Their various types—batch, continuous, and modular—offer unique advantages that can be tailored to the specific needs of different manufacturing operations.
By understanding the operational mechanics, benefits, and maintenance of quenching furnaces, manufacturers can optimize their production processes and achieve superior results. Investing in high-quality, durable quenching furnaces will undoubtedly yield long-term benefits, making them an indispensable asset in any metalworking facility.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the primary function of a quenching furnace?
The primary function of a quenching furnace is to rapidly cool heated metal components, allowing for the development of desired mechanical properties.
2. What types of materials can be treated with quenching furnaces?
Quenching furnaces can be used for a variety of metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper alloys, each with specific requirements for the heat treatment process.
3. How does the choice of quenching medium affect the outcome?
The choice of quenching medium—such as water, oil, or specialized fluids—affects cooling rates and can influence the final properties of the treated metal, such as hardness and toughness.
4. What maintenance practices should be employed for quenching furnaces?
Routine inspections, monitoring of temperature controls, cleaning of the quenching medium, and staff training are critical maintenance practices that enhance the furnace's performance and longevity.
5. What safety measures should be taken when operating quenching furnaces?
Operators should wear appropriate protective gear, follow established emergency protocols, and ensure adequate ventilation to mitigate hazards associated with the quenching process.